6 Strategies MSMEs can Adopt To Enhance Their Capabilities for Sustainable Growth
- Between 2000 and 2025, only 0.4% of micro-enterprises grew into small businesses, and a mere 0.05% of small companies managed to graduate into the medium enterprise category.
- Stagnation is largely due to weak capability building in people, processes, and systems, not just a lack of finance. This blog captures various ways in which MSMEs can improve their productivity, be future-ready, and resilient for any market conditions.
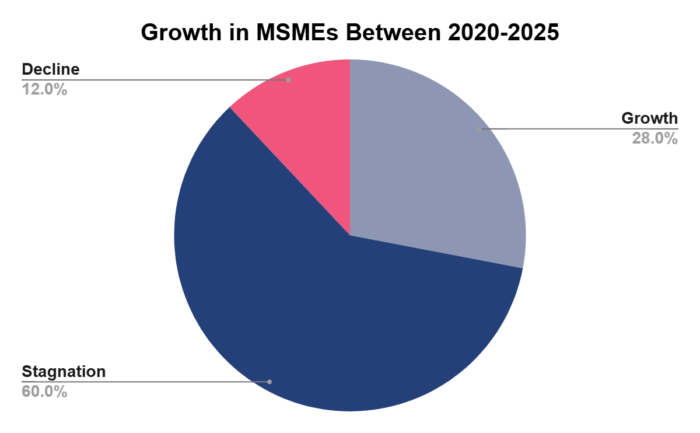
From 2000 to 2025, a meagre 0.4% of micro-enterprises grew into small businesses, and just 0.05% of small companies managed to graduate into the medium enterprise category1. Furthermore, only 28% of Indian MSMEs recorded a CAGR of 5–10% or higher. A majority, nearly 60%, remained stagnant, while about 12% experienced a decline during this period.
One of the primary reasons for this limited growth is the lack of systematic capability building. With tight profit margins, more than 60% of the MSME workforce is hired on a contractual basis. These employees are often less motivated to invest in upskilling themselves, leading to productivity levels rarely crossing 80%, and inconsistent quality.
Addressing this structural challenge requires MSMEs to enhance their capabilities in six interconnected capabilities: human capital, technology, finance, operations, markets, and institutional linkages.
1. Human Capital Development: Upskilling the Workforce
No enterprise can grow without the strength of its people. For MSMEs, which often operate with lean teams, workforce quality determines not only productivity but also customer satisfaction and competitiveness. However, the reliance on contract labor means skills are underdeveloped and accountability is limited. This is why human capital development must be seen as the foundation of capability building.
- Upskilling: The first step is upskilling and reskilling. MSMEs need to focus on both technical skills, such as machine handling and product design, and digital skills, such as using software for accounts or customer management. Managerial training is equally important to ensure supervisors can coordinate teams efficiently.
- Leadership Training: Another area is leadership and entrepreneurial training. Many MSME owners operate intuitively but lack structured training in decision-making, risk management, or long-term strategy. Targeted leadership programs can help owners and managers think beyond immediate challenges and plan for sustainable growth.
- Financial Literacy: Equally critical is financial literacy. Many entrepreneurs struggle to read balance sheets, calculate actual costs, or understand the implications of credit cycles. Training in basic finance can empower MSME leaders to make informed choices and avoid debt traps.
- Formalization: Finally, formalising the workforce through compliance with labor laws and ensuring workplace safety is essential. Formal employees are more invested in the enterprise’s success, leading to higher motivation and productivity.
2. Technology & Digital Capability: Building the Future-Ready Enterprise
MSMEs that continue to operate manually risk being left behind by competitors who leverage technology for speed, accuracy, and customer engagement. And in today’s economy, digital adoption is critical and helps MSMEs to leap forward in many ways.
- Digital Tools for Everyday Operations: One of the most accessible steps is the adoption of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems to help manage inventory and production, while Customer Relationship Management (CRM) tools streamline sales and service. Similarly, Digital invoicing and payments tools help give a clear visibility into cash flows, monitor any delayed or overdue payments, thereby helping businesses determine at what stage they need to consider loans for growth, survival or expansion.
- Industry 5.0 Readiness: This is relevant for MSMEs as it focuses on a symbiotic relationship between humans and machines, enhancing the workforce’s role rather than replacing it. While full-scale robotics or artificial intelligence may not be feasible for all, smaller applications such as Internet of Things (IoT) sensors for monitoring machines or AI-powered analytics for sales forecasting can deliver significant efficiency gains.
- E-Commerce Integration: Digital capability also extends to e-commerce integration. By onboarding with platforms like the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) and other platforms, MSMEs can reach new customers without heavy investment in physical infrastructure. This is particularly important for businesses in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities looking to tap into national and global markets.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Implementation of cybersecurity is crucial to safeguard MSMEs from any kind of data theft or fraud as they adopt more and more digital tools. Hiring specialised services, secure systems, and adopting basic safeguards can protect both business and customer information.
3. Financial & Credit Capability: Strengthening the Backbone of the Business
Financial stability is often the deciding factor between survival and closure for MSMEs. Many promising enterprises fail not because of poor products but due to poor financial management or lack of access to credit. Building financial and credit capability is therefore indispensable.
- Access to Affordable Credit: The most immediate requirement is access to affordable credit. Government initiatives can ease cash flow stress. Awareness of government and institutional schemes can make a real difference. Schemes such as the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) and the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme provide direct financial support or risk coverage. On the other hand, institutional programs run by agencies like the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) focus on broader developmental support, including capacity building and targeted lending. Many MSMEs miss out on these simply due to a lack of awareness and failing to maintain clean financial records to qualify for such initiatives.
- Cash Flow Management: Beyond credit access, effective cash flow management is vital for MSMEs. Delays in receivables often leave businesses vulnerable, making it important to plan reserves, monitor payables, and maintain discipline in expenses.
- Alternate Financing Solutions: Small enterprises must consider loans as a way to fuel growth ambitions and navigate turbulent times. Partnering with RBI-registered NBFCs like Protium ensures access to reliable financing that can support expansion while safeguarding stability.
4. Operational & Process Capability: Enhancing Efficiency & Quality
Even with skilled workers and financial stability, an MSME cannot thrive without robust processes. Operational discipline ensures that productivity improves while costs reduce, creating long-term competitiveness.
- Quality Management Systems: The first area is quality management. Certifications such as ISO and Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) are not just compliance badges but also signals of reliability for customers. Achieving and maintaining these certifications can open doors to larger contracts, both domestic and international.
- Lean Manufacturing Practices: Another important practice is lean manufacturing. By reducing waste—whether in materials, time, or processes—MSMEs can deliver higher output with fewer resources. This directly translates into higher profitability.
- Supply Chain Integration: For MSMEs, being part of a reliable supply chain can mean consistent orders and growth opportunities.. Connecting with Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) and developing strong vendor relationships ensures a steady flow of inputs and access to larger business networks.
- Sustainability Practices: Embracing sustainability practices such as energy efficiency, waste reduction, and green certifications is becoming essential. Not only do these reduce costs, but they also enhance brand reputation and meet the rising demand for environmentally responsible products.
5. Market & Customer Capability: Expanding Reach and Relevance
Building a capable enterprise is only half the journey; the other half lies in connecting with markets and customers. Without strong demand, even the most efficient operations cannot succeed. MSMEs, therefore, need to strengthen their ability to market, brand, and serve customers effectively.
Export Readiness: Becoming export-ready is one opportunity. By complying with international standards, mastering export documentation, and learning EXIM processes, MSMEs can tap into global demand. This reduces dependence on local markets and builds resilience.
Marketing and Branding: At the same time, marketing and branding are essential for differentiation. Storytelling, creative packaging, and clear product positioning can make a small business stand out in crowded markets. Customers are more likely to choose products that convey trust and quality.
Customer Service Excellence: Strong customer service is another pillar. After-sales support, timely response to complaints, and the use of CRM tools can build long-term loyalty. For MSMEs, repeat customers often account for a large share of revenue. Market intelligence allows MSMEs to stay ahead. Studying industry trends, monitoring customer preferences, and benchmarking competitors ensures that businesses remain relevant and competitive.
6. Institutional & Ecosystem Capability: Leveraging the Collective Strength
MSMEs rarely grow in isolation. Their ability to thrive often depends on the networks, institutions, and ecosystems they are part of. Building institutional capability means learning to leverage these collective strengths.
- Cluster Participation: Participation in clusters is one such strategy. Shared research and development facilities, testing labs, and common facility centers reduce costs and make advanced resources accessible even to small businesses.
- Corporate Partnerships: Partnerships with corporates provide access to larger supply chains. By becoming reliable vendors to big companies, MSMEs can secure consistent demand and exposure to higher standards.
- Policy Literacy: Developing policy literacy is equally important. Understanding rights, compliance requirements, and available benefits helps MSMEs avoid penalties and make use of supportive frameworks.
- Networking Platforms: Joining networking platforms such as industry associations or chambers of commerce provides opportunities to share knowledge, build credibility, and collaborate with peers.
Every investment in skills, systems, or networks lays the foundation for a stronger enterprise. The more MSMEs commit to building these capabilities, the more likely they are to scale consistently, deliver quality, and participate in India’s economic transformation. The roadmap is clear—strengthening capabilities is the key to long-term success.

