41% Auto Retail Sales Jump in October 2025: 5 Actionable Steps for MSMEs to Leverage the Boom
- With auto retail sales jumping 41% year-on-year, OEMs have increased production, boosting procurement from MSMEs across core component and fabrication units. The demand spike also creates immediate opportunities in the accessories and customization segment, while strengthening long-term recurring business in servicing, repairs, and replacement parts. At the same time, a wide set of support industries—from packaging and paint supplies to IT and workshop essentials—benefit indirectly as activity rises across the entire automotive ecosystem.
- Enterprises can capitalize on this momentum by adopting simple digital tools, improving vendor coordination, upgrading worker skills for advanced vehicular systems, accessing quick working-capital financing, and setting up small stocking hubs to reduce lead times and handle higher order volumes.
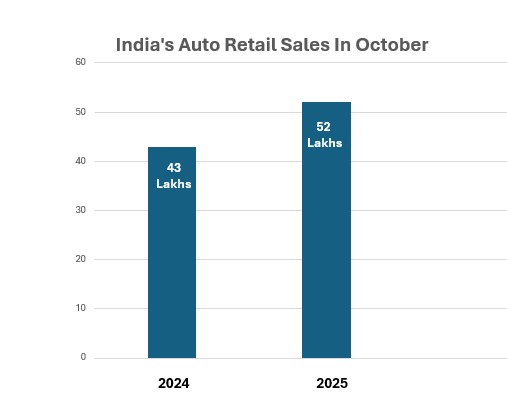
Automobile retail sales rose by a staggering 41% in October 2025 compared to the same period last year, marking the highest level ever recorded. The total vehicle sales crossed 52 lakhs from last year’s 43 lakhs, marking a 21% year-on-year increase1. The surge is fuelled by a robust demand for both passenger vehicles and two-wheelers, due to the GST rate dropping from 28% to 18% in September 2025, making purchases more affordable for first-time buyers and those upgrading their vehicles.
The impact of this sharp rise in demand extends well beyond large carmakers and their associated enterprises. The auto sector is built on a wide network of interconnected industries, and the auto sales boom activates multiple layers of immediate and long-term economic activity involving MSMEs. This includes small businesses across manufacturing, components, accessories, servicing, and logistics.
A strong sales performance also directly and instantly shapes how original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) plan production for the months ahead. When sales numbers are high, OEMs respond by increasing output, which immediately expands procurement requirements. This is especially relevant for MSMEs that supply components, assemblies, and raw materials. Small machining units, fabrication workshops, plastics and rubber processors, and electronics suppliers typically see a rise in inquiries soon after OEMs revise their production schedules.
Even a slight increase in production volume can create steady work for Tier-2 and Tier-3 suppliers, many of whom operate with small teams and limited automation. For these enterprises, consistent orders bring stability, predictable cash flows, and the chance to hire additional workers.
This blog article looks at all such interrelated benefits and how MSMEs can leverage the uptick.
How MSMEs in the Auto Supply Chain Benefit
MSMEs are the backbone of India’s automotive ecosystem, including the sector’s supply network. In fact, more than 70% of component manufacturers fall within the MSME category2. This means any shift in vehicle demand directly influences thousands of smaller units long before the final product reaches a showroom.
As OEMs scale up production, demand rises across several MSME-driven segments:
- Auto components such as brackets, sensors, small assemblies, clips, and connectors
- Metal fabrication, including frames, mounts, and body supports
- Machining units that produce precision components
- Rubber and plastic parts, from hoses and gaskets to molded interiors
- Small electronics, including wiring harness elements and switches
- Casting and forging units, supplying engine and transmission parts
This section of the value chain absorbs the first wave of demand whenever the market strengthens. For many MSMEs, even a modest uptick in orders creates room to upgrade equipment, buy better materials, or train workers, which strengthens their long-term competitiveness.
Small Businesses Powering the Automotive Aftermarket
The aftermarket is one of the strongest segments linked to new vehicle sales. When more vehicles enter the road, customers look for add-ons that improve comfort, safety, or style. MSMEs dominate this space through small workshops, upholstery units, and accessory shops spread across cities and towns.
The rise in vehicle sales expands the market for accessories and add-ons, creating steady demand across several categories. Customers look for new seat covers and upholstery in different materials, while floor mats tailored to seasonal conditions remain popular. Many buyers also upgrade their infotainment systems and audio setups, or opt for lighting enhancements such as LEDs and fog lamps. The focus on safety encourages purchases of sensors, dash cameras, and other protective accessories, and those seeking personalization often invest in body kits and custom paintwork. Together, these trends create a consistent flow of business for MSMEs operating in the aftermarket. The trend is particularly visible in Tier-2 and Tier-3 markets, where local workshops often serve as the first choice for customization because of their affordability and quicker turnaround times.
Servicing and Repairs Economy
As India’s vehicle base grows every year, it also creates a long-term servicing and repair requirement that lasts for the entire lifespan of the vehicle. MSMEs dominate this segment. Local garages, multi-brand service centers, tyre shops, and spare parts outlets are the primary service providers for most vehicle owners.
As the servicing and repair ecosystem expands, the movement of all these materials also begins to scale. Every increase in demand for consumables, tyres, batteries, and spare parts creates additional pressure on the transport network that supplies them. This forms a direct link between workshop activity and logistics, where rising volumes at garages and service centers translate into more frequent shipments across regions.
Logistics, Transport, and Mobility
Rising vehicle sales strengthen the transport and logistics network that moves cars, components, and accessories across the country. Delivering vehicles to dealerships, transporting spare parts, moving tyres from factories to retailers, and shifting paint supplies to workshops all require reliable logistics, much of which is handled by MSMEs.
This growth benefits:
- Small trucking companies transporting components
- Vehicle transporters delivering new cars to retail outlets
- Last-mile logistics providers carrying smaller loads
- Local warehousing and distribution agencies storing tyres, accessories, paints, and body-shop materials
As OEMs and component manufacturers expand operations, these MSMEs see higher freight volumes and better utilization of their small fleets. For many local transporters, steady movement of auto-related goods offers a secure income stream throughout the year.
Peripheral MSMEs Who Gain Indirectly
The impact of rising auto sales goes beyond manufacturing and logistics. A wide group of peripheral MSMEs experience secondary demand as auto-linked businesses scale up.
These include paint shops supplying body repair workshops, packaging vendors for safe shipment of parts, uniform and textile suppliers for service center staff, IT service providers handling billing, inventory, and appointment software, and Marketing and signage vendors supporting dealerships and accessory shops.
Each new vehicle on the road triggers activity across this extended network. Small enterprises that may not appear directly connected to the auto sector still benefit from the ripple created by higher sales and increased workshop demand.
How MSMEs Can Prepare for the Opportunity
As the auto boom continues, MSMEs need to be prepared to tap into the rising demand and respond to it quickly and reliably. This can be achieved by:
- Enhance Daily Operations for Higher Customer Volumes
Basic digital solutions can help MSMEs manage growing workloads more efficiently. Even simple applications for inventory tracking, billing, job cards, or order status updates reduce manual errors and provide better visibility into daily operations. This makes it easier to handle higher customer volumes during peak periods.
- Better Servicing and Production Vendor Coordination
Stronger coordination with suppliers becomes essential when demand increases. Clear communication and predictable ordering cycles help MSMEs avoid stockouts, maintain adequate supplies, and reduce delays in servicing or production. This ensures they can meet customer expectations without disruptions.
- Upgraded Skills for Advanced Vehicular Systems
The shift toward advanced vehicle systems requires workers trained in machining, electronics, EV servicing, and diagnostics. MSMEs with a skilled workforce can handle more complex jobs, offer higher-quality services, and stay relevant as technology in the auto sector evolves.
- Quick Financing for Larger & Frequent OEM Orders
Higher order volumes often require more working capital. Easy access to quick, flexible financing from RBI-regulated NBFCs such as Protium helps MSMEs buy materials on time, scale manpower, and manage cash-flow gaps during busy cycles. It also strengthens their ability to accept larger or frequent orders from OEMs.
- Small Storage or Stocking Hubs
Setting up compact storage areas or local stocking hubs in emerging auto clusters can significantly reduce lead times. By keeping frequently used parts, consumables, and accessories close at hand, MSMEs improve service speed and ensure consistent availability of essential items.
Strengthening these areas helps MSMEs meet higher order volumes, maintain delivery commitments, and build stronger relationships with OEMs and local customers. As India’s auto market is expected to maintain steady growth, backed by improved consumer sentiment and long-term industry projections, this is a chance for MSMEs to scale operations, modernize practices, and strengthen their place in one of India’s largest and most interconnected industries.

