India’s Credit Growth at 11.27%: Role MSMEs Play in Ensuring the Momentum Stays Strong
- With bank credit growth rising to 11.27%, lenders have more room to approve MSME loans quickly, which supports working capital, inventory purchases, and new orders.
- Automobiles, consumer durables, construction services, and local repair ecosystems are seeing continued movement, giving MSMEs more predictable order flows.
- As financial institutions such as RBI-registered Protium expand their loan books, MSMEs stand to gain from quicker processing, better repayment terms, and products tailored to their business cycles.
- Regular GST filings, Udyam registration, and cleaner digital records are helping lenders assess small businesses more accurately, increasing approval chances.
- With credit growth expected to remain between 10% and 12%, businesses with strong records and clear financial planning can upgrade machinery, manage cash flow better, and prepare for higher demand in 2025.
India’s credit growth moved up to 11.27% year-on-year by mid-October 2025, supported by increased household purchases, GST reductions on specific product categories, and a strong rise in loan disbursements during the festive season. Nearly ₹3 trillion in incremental loans were disbursed in a single month, reflecting a sharp revival in borrowing activity1. For MSMEs, especially in Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities, this shift matters because it signals an improvement in credit availability at a time when business demand, inventory cycles, and capacity utilization are rising.
The festive period was a major contributor to the rise in lending. Increased interest in vehicles and appliances encouraged households to borrow more, and this activity supported production, distribution, and service networks that involved a large share of MSMEs. With GST cuts improving product affordability, customers advanced their purchases, which boosted order volumes for several small businesses.
As borrowing gained momentum after a slower phase earlier in the year, the focus has now moved to whether this pace can continue—along with what it will mean for MSMEs preparing for 2026.
Structural Factors Sustaining the Credit Momentum
While the festive surge played its part, several broader factors continue to support the credit momentum.
- Lower GST rates on automobiles and consumer durables: This has helped maintain demand even after the season, ensuring that manufacturers, component suppliers, logistics operators, installers, and repair units experience consistent business movement.
- Liquidity conditions in the banking system: With a stable availability of funds, lenders can process credit applications with fewer delays and greater confidence.
- Supportive mechanisms such as guarantee-backed structures: These ease lenders’ concerns, encouraging them to extend formal credit to smaller businesses. As MSMEs formalize their operations through Udyam registration, regular GST filing, and improved digital record-keeping, their eligibility for loans has naturally strengthened.
For small enterprises, these conditions create an environment where borrowing becomes more predictable and more closely aligned with operational needs.
MSMEs at the Center of Lending Growth
The rise in formalisation is visible in official records. Udyam registrations increased from 2.5 crore in March 2024 to more than 6.5 crore by June 2025, widening the base of enterprises with verifiable documentation. As more MSMEs enter the formal system, lenders can assess turnover patterns, GST compliance, and transaction trails with much greater clarity. This shift has been supported by digital onboarding, with video KYC and online verification now forming a majority of new loan account openings across the financial sector. These processes reduce delays and make it easier for small businesses to access credit.
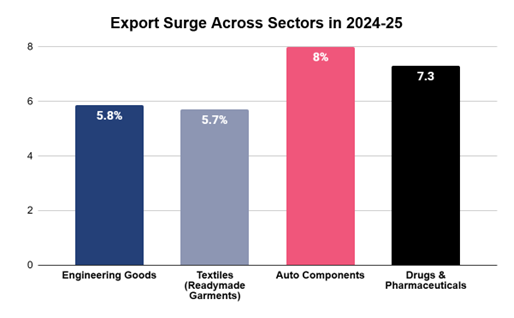
Sectoral indicators also show movement in industries where MSMEs form a large part of the supply chain. For instance, engineering goods grew by around 5.86% year-on-year during the April–August 2025 period, readymade garments in textiles were up by 5.78%, and drugs and pharmaceuticals by 7.30%. This reflects steady demand across key markets and consistent activity in sectors where MSMEs contribute significantly through manufacturing, fabrication, packaging, logistics, and contract services.
For MSMEs, this means lenders now view them as an active part of the growth cycle, rather than an optional segment. This improves both access to funds and institutions’ willingness to create small-business-focused loan products.
This credit expansion is reflected in sectors such as the automobile, with higher two-wheeler and car purchases benefiting component manufacturers, welding units, repair workshops, tyre distributors, and battery retailers. Purchases in consumer durables are also supporting small businesses involved in packaging, appliance installation, cable production, logistics, and small electronic components. Similarly, construction-related services, including carpentry, plumbing, electrical work, fabrication, and small contracting, have maintained a steady need for working capital.
The spread of activity across these sectors offers MSMEs practical clarity on where market opportunities may expand. Businesses positioned in these value chains can use this phase to strengthen inventory planning, upgrade equipment, or take on additional orders with greater confidence.
What MSMEs Can Expect in the Coming Quarters
Current projections suggest that bank credit growth may remain between 10% and 12% over the next few months. This expectation is supported by stable household demand, continued interest in vehicles and consumer appliances, and higher capacity utilization among small manufacturers and service providers. As MSMEs operate closer to full capacity, their requirements for working capital, raw-material finance, and equipment upgrades are set to increase.
A phase of sustained credit growth carries several direct benefits for MSMEs.
- Improved loan approval rates: As banks expand their loan books, approval rates for small-business credit tend to improve, especially for enterprises with consistent financial records. Faster disbursals help MSMEs manage inventory cycles, secure raw materials at the right time, and meet short project timelines. Businesses that have delayed repairs or machinery purchases due to cautious lending earlier in the year may now find lenders more responsive.
- Higher credit activity: This encourages financial institutions to provide better product flexibility and more tailored repayment structures for small businesses. When more credit flows through the economy, payment cycles often improve, reducing delays and helping MSMEs maintain smoother cash flow. Overall, this environment allows MSMEs to strengthen operations, expand capacity responsibly, and build financial stability as they plan for 2026.
How MSMEs can Ensure the Growth Sustains
As lending momentum strengthens across the financial system, MSMEs play an important role in ensuring that this growth continues. Credit expansion is not driven by lenders alone; it is sustained when small businesses build predictable financial behaviour, maintain strong documentation, and use credit productively. The following practices help reinforce that momentum and keep MSMEs firmly integrated into India’s credit cycle.
- Strengthening Financial Visibility
MSMEs can help sustain the current pace of lending by ensuring that their financial activity is clearly visible to banks and NBFCs. When sales, purchases, GST filings, and payment flows reflect consistency, lenders gain accurate insight into the business. This clarity reinforces the belief that small enterprises are dependable borrowers, encouraging institutions to continue expanding credit to the segment.
- Using Credit Productively
Credit growth remains strong when MSMEs use borrowed funds for activities that improve output and efficiency—such as machinery upgrades, inventory management, or service expansion. When lenders observe measurable operational improvements and steady repayment behaviour, they become more confident in allocating higher credit limits to similar businesses across the sector.
As more MSMEs build consistent repayment behaviour through institutions like Protium, the overall credit ecosystem becomes stronger, more transparent, and better equipped to support long-term lending momentum.
- Deepening Participation in Formal Platforms
Wider adoption of formal financial tools such as TReDS and CGTMSE, and digital payment systems strengthens the overall lending ecosystem. As more MSMEs build verifiable transaction histories and reduce reliance on cash-based operations, the risk perception around the segment declines. This creates a more favourable environment for sustained credit expansion.
- Maintaining Disciplined Borrowing Practices
Regular repayment, minimal cheque bounces, and timely servicing of EMIs are essential for keeping credit growth steady. When MSMEs demonstrate repayment discipline at scale, lenders gain confidence that the segment can support larger loan books without increasing risk. This helps ensure that credit availability remains stable even during periods of market fluctuation.
Borrowing through RBI-regulated NBFCs such as Protium further reinforces this shift. When MSMEs access formal credit products, whether through Business Loans for working capital, Machinery and Equipment Loans for capacity building, or long-term solutions like Loan Against Property and Top-Up Loans, they create a documented borrowing and repayment record that strengthens their creditworthiness over time. NBFCs also offer faster processing, local-market understanding, and product structures aligned to MSME business cycles, helping enterprises transition away from informal lenders.
- Planning for Future Demand
Lending momentum strengthens when MSMEs approach financing with a forward-looking mindset. Businesses that prepare for upcoming demand cycles, by assessing capacity, planning equipment upgrades, or building workforce capabilities, signal long-term stability to lenders. This proactive behaviour encourages financial institutions to keep prioritising the segment as a core driver of credit growth.

